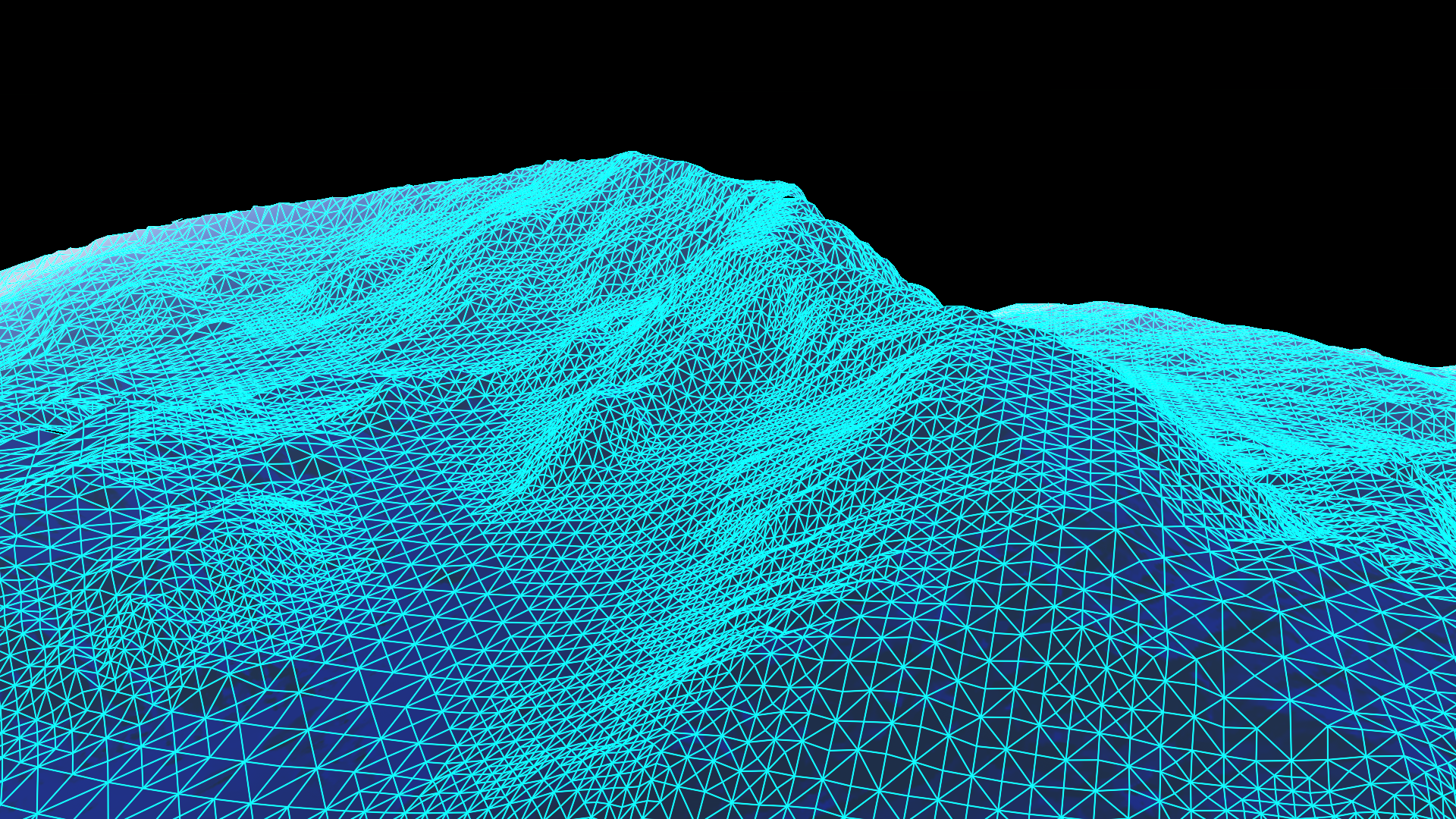
Terrain¶
The Alire crate orka_plugins_terrain provides packages to render adaptively tessellated terrain of a planet on the GPU.
-
Updates and renders multiple terrain tiles and uses heuristics to determine on the CPU which tiles need to be updated and rendered.
-
Supports flattened spheroids with warping to reduce RMSE when projecting cubes on spheres.
-
Can optionally display a wireframe on top of the rendered terrain.
Info
The various objects described on this page are declared in
the package Orka.Features.Terrain and its child packages.
Creating terrain¶
To render the terrain, first create some location objects containing the shaders of the crate:
Location_Data : constant Locations.Location_Ptr :=
Locations.Directories.Create_Location ("data");
Location_Terrain : constant Locations.Location_Ptr :=
Locations.Directories.Create_Location ("path/to/orka_plugin_terrain/data/shaders");
Location_Data should point to a location containing the terrain/ directory,
which should contain the height and slope map textures.
- The height map is
RG16(2xUnsigned_16) (about 86 MiB) orCOMPRESSED_RG_RGTC2(about 17 MiB). - The slope smap is
RG32F(2xFloat_32) (about 171 MiB) orCompressed_RGB_BPTC_Signed_Float(about 22 MiB).
Configuration¶
To adaptively tesselate terrain, some parameters are needed which specify how much the terrain should be tesselated:
Terrain_Parameters : Subdivision_Parameters :=
(Meshlet_Subdivision => 3,
Edge_Length_Target => 16,
Min_LoD_Standard_Dev => 0.00);
Terrain_Min_Depth : constant := 6;
Terrain_Max_Depth : constant := 20;
Displace_Terrain : constant Boolean := False;
The maximum tesselation is controlled by the constant Terrain_Max_Depth.
Increase this constant to further subdivide the terrain.
However, older GPUs might not be able to handle values greater than 20.
A maximum depth of 20 might be too low
Intel GPUs cannot handle very large max terrain subdivision levels,
which limits the maximum terrain resolution.
Currently the maximum Terrain_Max_Depth is set to 20.
Discrete GPUs might handle larger values.
A value of 20 gives a resolution of about 2 km per triangle.
A way needs to be found to also render terrain with a higher resolution
when the camera is close to the surface.
Either replace the (up to) 5 tiles with 1 to 3 smaller tiles (3 when
viewing a corner of the Earth cube) or have 1 extra very small tile that
is always somewhat in the center of the screen (between the camera and
the center of the Earth).
Creating helpers¶
Create Terrain and Terrain_Planet objects by calling the functions
Create_Terrain and Create_Terrain_Planet:
Terrain_1_Planet : Terrain_Planet :=
Create_Terrain_Planet
(Earth_Data, Planets.Earth.Planet,
Cached_Atmosphere, Location_Data, Location_Terrain);
procedure Initialize_Atmosphere_Terrain_Program
(Program : Orka.Rendering.Programs.Program) is
begin
Program.Uniform_Sampler ("u_DmapSampler").Verify_Compatibility
(Terrain_1_Planet.Height_Map);
Program.Uniform_Sampler ("u_SmapSampler").Verify_Compatibility
(Terrain_1_Planet.Slope_Map);
end Initialize_Atmosphere_Terrain_Program;
Terrain_1 : Terrain := Create_Terrain
(Count => 6,
Min_Depth => Terrain_Min_Depth,
Max_Depth => Terrain_Max_Depth,
Scale => (if Displace_Terrain then 1.0 else 0.0),
Wireframe => True,
Location => Location_Terrain,
Render_Modules => Terrain_1_Planet.Render_Modules,
Initialize_Render => Initialize_Atmosphere_Terrain_Program'Access);
Rendering¶
Create two timers:
Timer_Terrain_Update : Orka.Timers.Timer := Orka.Timers.Create_Timer;
Timer_Terrain_Render : Orka.Timers.Timer := Orka.Timers.Create_Timer;
Some variables can be defined to control whether the wireframe must be shown and whether the terrain must be updated when the camera changes its position:
Freeze_Terrain_Update : Boolean := False;
Show_Terrain_Wireframe : Boolean := True;
Finally, render the terrain with procedure Render:
declare
Visible_Tiles : Natural := 0;
begin
Terrain_1_Planet.Render
(Terrain => Terrain_1,
Parameters => Terrain_Parameters,
Visible_Tiles => Visible_Tiles,
Camera => Camera,
Planet => Planet,
Star => Sun,
Rotation => Orientation_Planet,
Center => Translation_Planet,
Freeze => Freeze_Terrain_Update,
Wires => Show_Terrain_Wireframe,
Timer_Update => Timer_Terrain_Update,
Timer_Render => Timer_Terrain_Render);
end;
In the variable Visible_Tiles the number of tiles which are visible will be stored.
The Camera needs to be a Camera_Ptr (defined in package Orka.Cameras)
and Planet and Sun need to be pointers to two objects implementing
the interface Behavior (defined in package Orka.Behaviors).
Orientation_Planet should be a Matrix4 describing the desired rotation
of the planet.
Translation_Planet should be a Matrix4 describing the translation
from the camera's view position to the center of the planet, divided
by Earth_Data.Length_Unit_In_Meters:
T ((Planet.Position - Camera.View_Position) * (1.0 / Earth_Data.Length_Unit_In_Meters)`
See Transformations for more information.
The directory terrain/ in the location Location_Data should contain
the file terrain-render-atmosphere.frag. This fragment shaders should
implement the function vec4 ShadeFragment(vec2 texCoord, vec4 worldPos).
Unexpected amount of subdivision
The terrain code originally worked only on a single flat tile, without any
problems. To render a planet, 6 tiles are needed (of which only 2 to 5 can
be visible). These tiles are also curved and then warped to reduce the RMSE
when projecting cubes on spheres.
When you zoom out and view the planet at a distance, some parts of each
tile like the center or corners get less or more subdivisions than you
would expect based on the distance from the camera to the surface. This
problems shows up more clearly when you change Meshlet_Subdivision to 1.
Frustum and occlusion culling is partly broken
Frustum and occlusion culling (in data/shaders/terrain/terrain-update-lod.comp)
might need to be fixed when terrain is displaced.
All tiles use a single height and slope map
All tiles currently use two textures in data/terrain/texture-4k-dmap.ktx
(height map) and data/terrain/texture-4k-smap.ktx (slope map), accessed
through the location object Location_Data.
To get the actual terrain of the Earth rendered, NASA SRTM DEM data is
needed, converted to an Unsigned_16_Array (for the height map)
and Float_32_Array for the slope map, and then written to .ktx textures.
See data/shaders/terrain/terrain-render-sphere.glsl for how a point on a
plane or tile is changed to a point on a sphere.
Screenshots¶
Triangle culling of terrain is based on the frustum and the distance from camera:
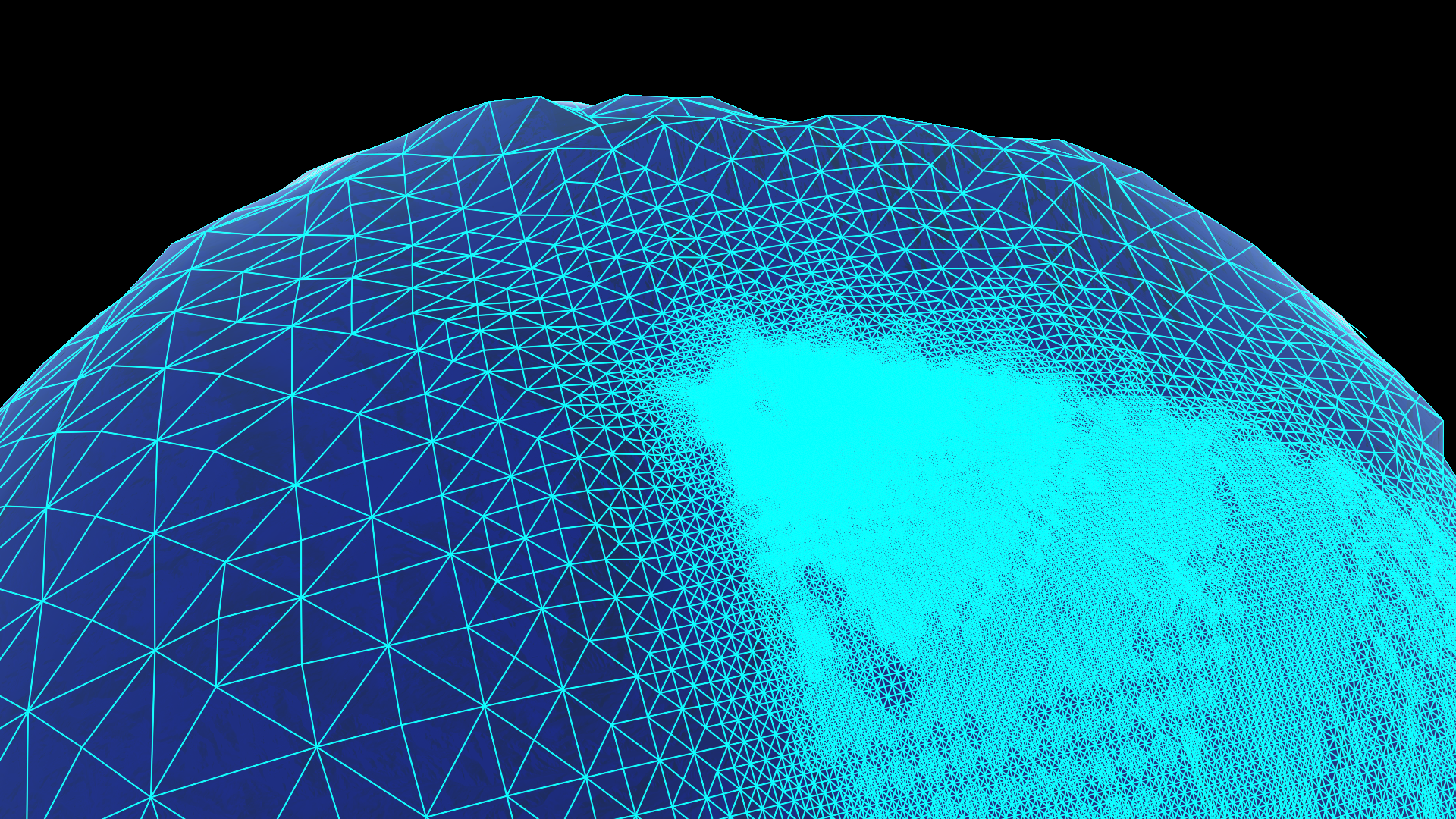
Increase the minimum level of detail (LoD) variance to reduce the number of triangles on flat terrain: